Bitumen viscosity test measures viscosity of bitumen.
Viscosity is an important physical property of bitumen and shows how easily bitumen flows.
Different methods can obtain viscosity of bitumen. Read this article to learn about different bitumen viscosity tests, its importance, and standards.
What is Bitumen Viscosity Test?
Bitumen viscosity test is one of bitumen tests. The goal of this test is to measure dynamic and kinematic viscosity of bitumen. The test can be performed using different methods and at different temperatures.
What is the purpose of Bitumen Viscosity Test?
Viscosity of bitumen is one of the important properties that must be tested because knowing the viscosity of bitumen helps to:
- Set the right temperature for mixing bitumen with aggregate in asphalt mixture
- Choose the best bitumen type and grade for the project
- Predict the performance of bitumen in different conditions
- Create long-standing road pavements
- Prevent cracking of asphalt in cold weather and rutting in hot weather
Types of Viscosity
In bitumen viscosity testing, two main types of bitumen are important:
Dynamic or Absolute Viscosity
Dynamic viscosity is a measure of the resistance of fluid to flow when a force is applied to it.
It is the ratio of shear stress and shear rate.
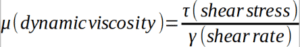
Dynamic viscosity is reported in Pa·s, poise (dyne·s/cm2), and centipoise (cP).
Kinematic Viscosity
Kinematic viscosity, or kinetic viscosity, shows the resistance of fluid to flow under gravity force. It is the ratio of fluid dynamic viscosity to its density:
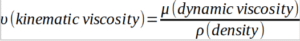
Its units are Stokes (St), centistokes (cSt), and m2/s.
Standards for Viscosity Tests of Bitumen
There are several standards for the viscosity test of bitumen:
Dynamic or absolute viscosity
- ASTM D4402
- EN 13302
- AASHTO T202-03
- IS 1206 (II)
Kinematic viscosity
- ASTM D2170
- ASTM D445
- EN 12595
- AASHTO T201-03
- IS 1206 (III)
Bitumen Viscosity Tests
Dynamic Viscosity Tests
The absolute or dynamic viscosity of bitumen can be measured using different tests like sliding plate viscometer, rheometer by cone and plate, and rotary viscometer. Below, you can read more about these methods of dynamic viscosity test for bitumen.
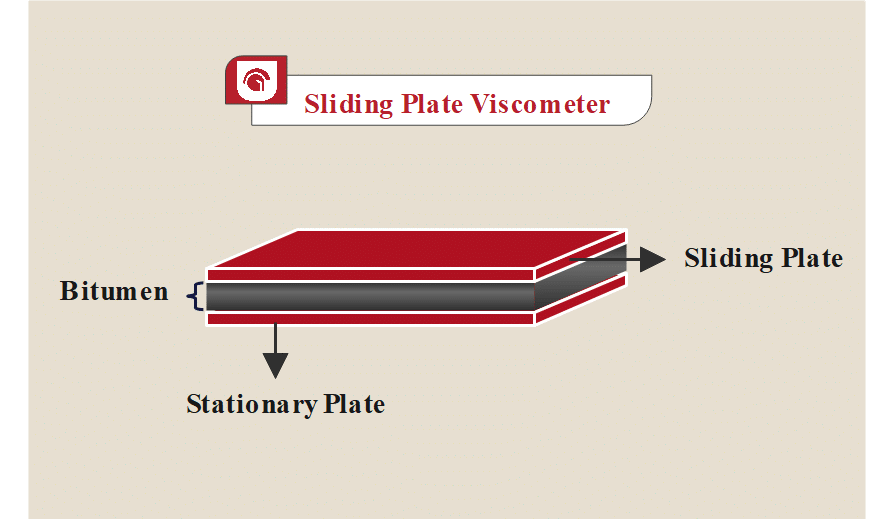
1. Bitumen Viscosity Test with Sliding Plate Viscometer
A common method for measuring bitumen viscosity is a sliding plate viscometer.
This method measures bitumen dynamic viscosity in low temperatures (typically in the range of -10°C to 50°C).
This viscometer has two parallel plates. Bitumen sample with thickness of 5 to 50 mm is placed between them. The upper plate slides over the bitumen, while the lower plate remains stationary. In fact, the upper plate applies shear stress to the bitumen. The shear rate is reported. Then, the viscosity is obtained.
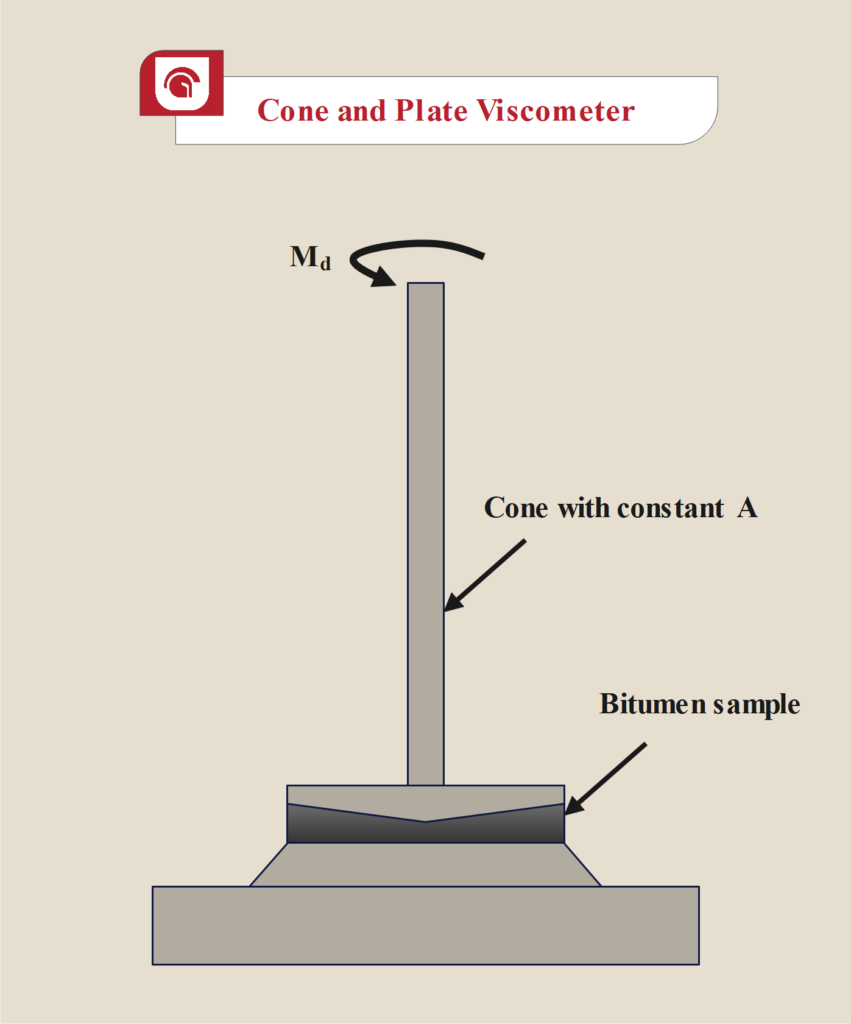
2. Bitumen Viscosity Test with Rheometer (Cone and Plate method)
Using rheometer by cone and plate is another way to obtain bitumen absolute viscosity.
The rheometer has a plate and a cone. Bitumen sample is placed on a plate and the cone is pressed onto the bitumen. Then, the system reaches the defined temperature. The range of temperature is 60 °C to 180 °C.
By setting the rotating speed, the cone starts to rotate. Using a known torque and cone factor, the testing system calculates the absolute viscosity of bitumen.
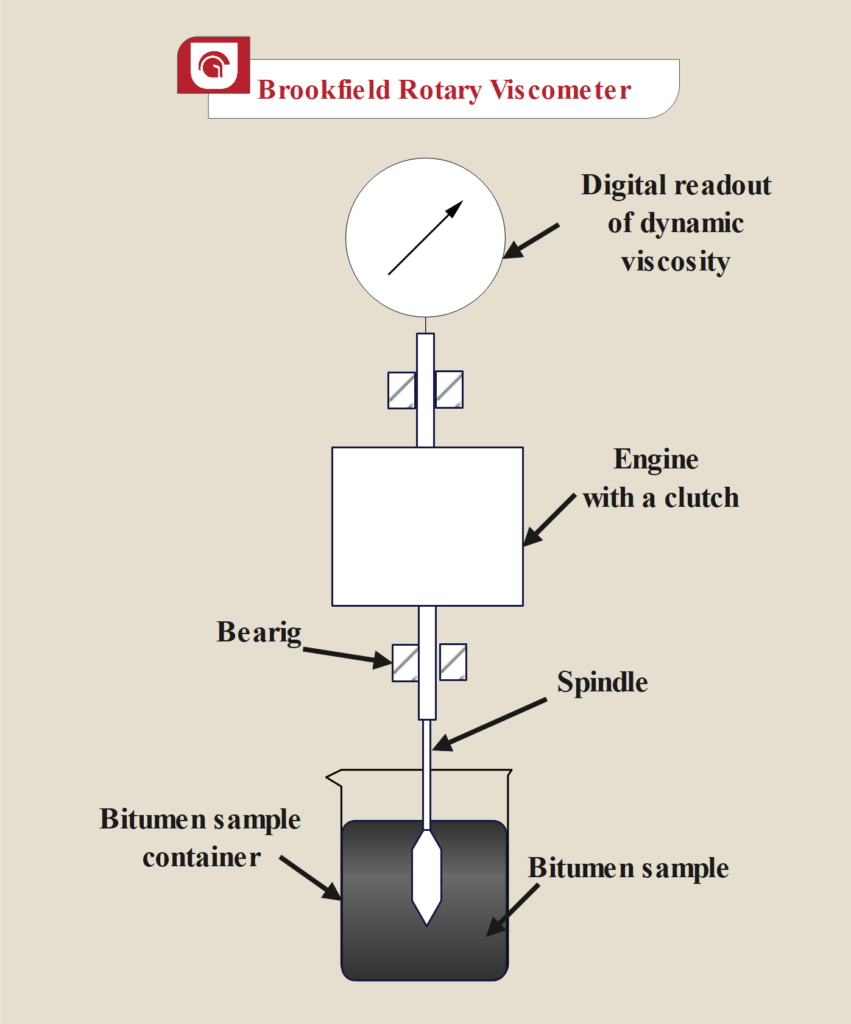
3. Bitumen Viscosity Test with Brookfield Rotary Viscometer
Rotational viscometer, like Brookfield rotary viscometer, is a tool to measure bitumen viscosity in high temperatures.
Brookfield viscometer has a thermal chamber and spindle.
The thermal chamber controls and keeps bitumen temperature at desired temperature.
The spindle is immersed in bitumen and rotates at a constant speed.
The viscometer measures the required torque to spindle rotates with constant speed in bitumen. This measurement will be converted to bitumen absolute viscosity in Pa.s or cP.
Brookfield rotary viscosity test is usually performed at 150°C, but it can be performed between 40°C to 260°C.
Kinematic viscosity tests
Kinematic viscosity of bitumen is measured by capillary viscometer. Continue reading to learn about this method.
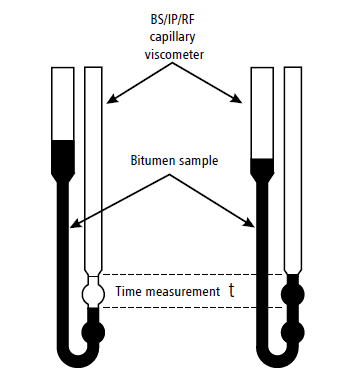
Bitumen Viscosity Test with Capillary Viscometer
Capillary viscometer is a common method for measuring kinematic viscosity of bitumen.
This viscometer is a U-shaped glass tube with wide and narrow parts. It has a capillary section and timing bulbs (marked sections for timing).
Bitumen sample is heated to test temperature (60°C or 135°C), and viscometer is filled with bitumen in the broader part of it. From the other arm of viscometer, we use suction to flow bitumen in the other arm up to marked level. After that, let bitumen flow down under gravity and the time which taken for bitumen to pass between two time marks is recorded.
This time is multiplied by a constant value to obtain kinematic viscosity of bitumen.
Factors Affecting Bitumen Viscosity
Several factors affect bitumen viscosity:
- Bitumen grade
- Temperature
- Aging and oxidation
- Modifiers
Bitumen Grade
Bitumen is classified based on viscosity value at 60°C or 135°C into different grades. Viscosity grade bitumen is a type of bitumen in which bitumen is graded based on viscosity: VG 10, VG 20, VG 30, and VG 40. The number after VG is an indicator of viscosity. The higher the viscosity of bitumen, the higher the number.
In the table, you can see the bitumen viscosity for different viscosity grade bitumen.
Bitumen viscosity for different viscosity grade bitumen | ||
Bitumen Grade | Dynamic viscosity, 60°C, poises | Kinematic viscosity, 135°C, cSt |
VG 10 | 800 | 250 |
VG 20 | 1600 | 300 |
VG 30 | 2400 | 350 |
VG 40 | 3200 | 400 |
Temperature
Bitumen viscosity highly depends on temperature.
By increasing temperature, forces between molecules become weaker, and molecules can move more freely. Therefore, bitumen viscosity decreases with increasing temperature.
For example, the viscosity of penetration grade bitumen 50/70 at 60°C is 1000 Pa·s while at 80°C is 100 Pa.s.
Aging and Oxidation
When bitumen is in contact with air, it reacts with oxygen in the air and slowly oxidizes. This oxidation causes the formation of a larger chemical group in bitumen, making bitumen harden. After oxidation, bitumen has higher viscosity.
Modifiers
Modifiers like polymer are sometimes added to bitumen to improve its properties. Polymer changes the bitumen viscosity and often increases the dynamic and kinematic viscosity.
However, the amount of additive and increase in bitumen viscosity is not direct.
FAQ
Viscosity of bitumen is an important property of bitumen and depends on temperature. Viscosity testing helps ensure the bitumen used is durable at different temperature conditions. For example, in colder regions, selecting bitumen with the right viscosity prevents cracking, while in hotter climates, it reduces the risk of rutting. It also helps engineers choose the right bitumen grade to have a proper mixing with aggregates for a strong asphalt mixture.
