Bitumen is a dark and viscous liquid that is derived from petroleum. Bitumen has different types and grades and each of them is suitable for specific applications. One of its major applications is in road construction.
In the following, we review the types of bitumen and different layers of road construction. Also, we consider types of bitumen used in road layers and discuss factors that influence bitumen selection.
Types of Bitumen
Several types of bitumen are used in road construction. Each of them has specific properties and is suitable for particular conditions. The following are the main types:
Penetration Grade
Penetration grade bitumen is classified based on penetration and softening point.
It is indicated based on two numbers, for example, 30/40. These numbers show the penetration depth range in tenths of a millimeter of a needle at 25 °C.
This type of bitumen is widely used in road construction.
Viscosity Grade
Viscosity grade bitumen is classified based on bitumen viscosity at 60 °C. It is indicated with VG and the following number. The number shows the viscosity in poises. For example, VG10 is a viscosity grade bitumen with a viscosity equal to 10 poises. This type of bitumen is suitable for use in road construction.
Bitumen Emulsion
Bitumen emulsion is a mixture of bitumen, water, and emulsifiers. The bitumen droplets are suspended in a continuous water phase with the assistance of an emulsifier.
There are different bitumen emulsion types: anionic, cationic, and nonionic bitumen emulsion. This type of bitumen can be used in lower-temperature and cold asphalt mixtures.
Cut back Bitumen
Cutback bitumen is a type of bitumen produced by blending penetration-grade bitumen and petroleum solvents. This blending reduces the viscosity of bitumen and makes it good for use in lower temperatures. Therefore, it is a suitable types of bitumen for road construction in cold regions.
Modified Bitumen
In modified bitumen, some additives are added to bitumen to improve its properties. Polymer is one of the additives. Polymer-modified bitumen is resistant to rutting, temperature fluctuation, and cracking. These improvements make it an ideal choice for use in road pavement.
Layers of Road Construction
In road construction, there are seven layers, three main layers and four sublayers. The main layers are:
- Surface course
- Base course
- Sub-base course.
Sublayers include:
- Tack coat
- Binder course
- Prime cat
- Capping layer.
The following figure shows the schematic of different road layers.
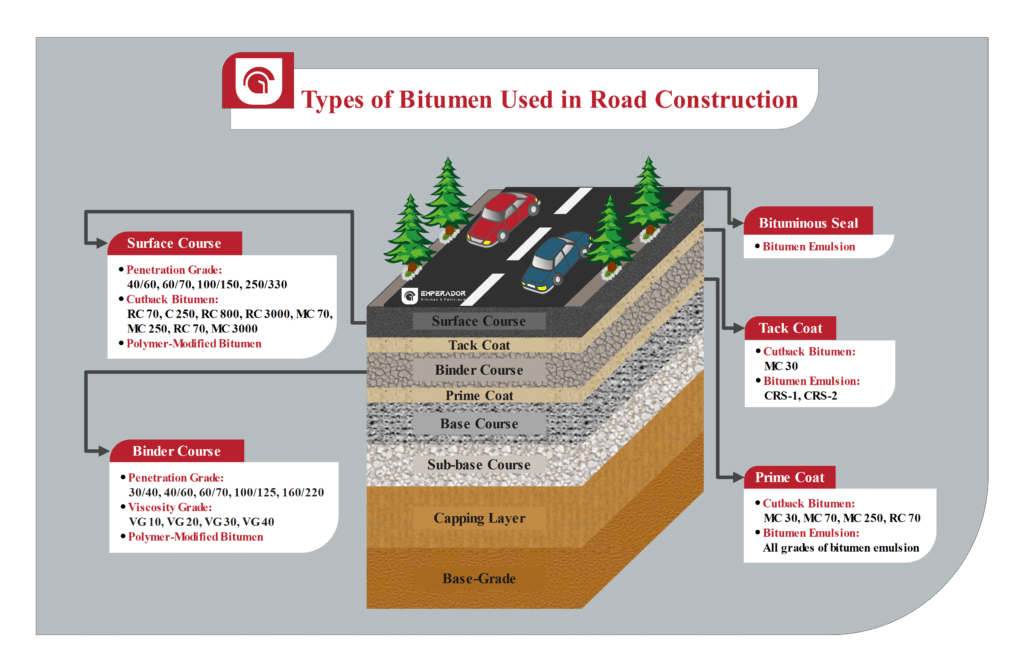
The layers of the road from bottom to top are as follows:
Sub-grade
Sub-grade or roadbed is the part of the ground that is the foundation of a road. Other road layers are placed on the sub-grade to make the road. Therefore, it is an important part of the road structure and it must be strong.
Capping layer
When the sub-grade soil is weak, the capping layer is used to provide a stable foundation for pavement construction. It is an optional layer that is located directly on top of sub-grade.
Sub-base Course
Sub-base course is one of the main road layers. It lies over the sub-grade (or capping layer if provided). It is between sub-grade and base course. The objective of this layer is to reduce stress applied to the subgrade by spreading the pressure over the sub-grade. The other objective is to prevent fines from sub-grade to go on upper layers.
Sub-base consists of crushed stone or gravel of river bed and is 100-300 mm thick. This layer can be unbounded or treated to be stabilized using stabilizers such as cement, ash, and lime.
Base Course
The base course is the other main road layer and is placed above the sub-base course. It immediately lies below the asphalt. Its thickness is about 100-300 mm.
It consists of crushed stone or natural gravel and is, in many cases, treated (stabilized) with a bitumen emulsion, lime, or cement to improve its road-building qualities.
Prime coat
The prime coat is on the top of the base course. The base course is loose and a prime coat is used to harden it. In the prime coat, a thin layer of bituminous liquid is sprayed on the top of the base course. In addition, this layer prevents it from rising to asphalt layers.
Binder course
The binder course is placed between the base course and the surface course. Binder courses have coarse aggregates and bitumen. It provides additional load distribution and is a key structural component.
Tack coat
A tack coat is a thin layer of liquid bitumen that is placed on top of the binder course. It bonds two asphalt layers.
Surface course
The surface course is the top layer of the road and is in contact with the vehicles. This layer is composed of smaller aggregates rather than a binder course. It must be durable and safe.
Bituminous seal
Over time, asphalt can be damaged because of rainfall, chemicals, sunlight, etc. Sealing the asphalt acts as a protective layer for asphalt pavement. Different types of protection are:
Slurry seal
Slurry sealing is a seal obtained by the combination of bitumen and fine aggregates. It can protect the asphalt from oxidation.
Chip seal
Chip seal is a surface treatment that provides waterproofing and crack sealing. It consists of bitumen and chips.
Different Types of Bitumen Used in Different Road Layers
In road construction, bitumen is used in some road layers. It is necessary to know which type of bitumen is used in road layers. Following the types and grades of bitumen used in each road layer.
Different types of bitumen in prime coat:
Cut back bitumen: MC 30, MC 70, MC 250, RC 70
Bitumen emulsion: All grades of bitumen emulsion
Different types of bitumen in binder course:
Penetration grade: 30/40, 40/60, 60/70, 100/125, 160/220
Viscosity grade: VG 10, VG 20, VG 30, VG 40
Modified bitumen
Different types of bitumen in tack coat:
Cut back bitumen: MC 30
Bitumen emulsion: CRS-1, CRS-2
Different types of bitumen in surface course:
Penetration grade: 40/60, 60/70, 100/150, 250/330
Cut back bitumen: RC 70, C 250, RC 800, RC 3000, MC 70, MC 250, RC 70, MC 3000
Modified bitumen: polymer-modified bitumen
Different types of bitumen in bituminous seal
Bitumen emulsion
Factors Influencing Bitumen Selection
Some factors influence the choice of right bitumen for road layers such as climate conditions like temperature and traffic load.
Temperature
Temperature fluctuations play an important role in choosing the right bitumen grade for different road layers. Proper bitumen selection based on local climate conditions can significantly improve road durability and performance.
Hot climate bitumen selection:
Bitumen’s dark color causes it to absorb solar radiation. Therefore, in tropical or desert environments, asphalt road temperatures can reach up to 20-30°C hotter than the surrounding air. For example, in Morocco the maximum temperature can exceed 50 C and surface road temperature can reach to 80 C.
This high temperature leads to:
Asphalt deformation
Accelerated aging
Rutting asphalt layer.
In hot climates, a bitumen with lower penetration value is suitable and preferred for enhanced stability.
For example, polymer-modified bitumen is resistant to deformation in high temperatures.
Cold climate bitumen selection:
In cold places like Canada and northern Europe, the bitumen in roads can become very hard when temperatures drop. This makes the road surface brittle and easy to crack. The constant freezing and thawing of water in the ground also harms the road layers underneath.
This cold temperature leads to:
Increased brittleness of the road surface
Low-Temperature Cracking
In cold climates, bitumen with a higher penetration value is preferred.
For example, VG10 is a recommended bitumen grade for cold conditions.
Traffic Load
It is necessary to consider traffic volume and load capacity in choosing bitumen for road construction projects. The bitumen should withstand heavy traffic and high loads of vehicles. When a heavy load is applied to a pavement, several stresses will apply to the asphalt layer. Therefore, the road layers should be strong and resistant to the stresses to prevent deformation.
Otherwise, the asphalt will have:
Cracking
Aging
Deformation.
In regions with high traffic volume, heavy vehicles cause considerable damage to the road. Bitumen with higher resistance to ruts and cracks is needed on roads with high traffic volumes or heavy vehicles such as trucks.
For instance, polymer-modified bitumen is the right choice for heavier traffic roads.
But for rural roads with low traffic volumes, asphalt must be able to withstand temperature changes.
Selecting the suitable bitumen based on these factors helps to:
Increase durability: right bitumen is resistant to temperature change and makes road last longer
Eco-friendly: less need for repair means fewer resources.
Cost-effectiveness: reduce the need for repair.
FAQ
Prime coat and tack coat are two sublayers in road construction. In both of them, a thin layer of liquid bitumen is used. The prime coat is placed above the loose base course and is used to harden the base. While the goal of a tack coat is to bond two asphalt layers.
In cold regions, bitumen with a higher penetration value is preferred. This bitumen prevents the cracking of the asphalt surface.
